Whatever the reason why the battery terminal is heating up, it is not good. The problem needs to be found and solved urgently. If the defect is not noticed and corrected in a timely manner, then the insulation of power cables will melt due to severe overheating, the plastic parts of the battery will leak, and even the terminal itself may turn into a shapeless pile of lead. A fire is also possible.
On the other hand, this topic is quite interesting, since many find it difficult to understand, find and eliminate the cause of inadequate heating of the battery terminals. Why is this happening? What is the reason? Where to look for a defect? Often, car enthusiasts try to turn to long-forgotten laws from school physics, which often causes confusion rather than leading to an understanding of the problem. Although this is the right direction. That's why we'll start with it.
A little school physics (in simple words)
What physical quantities, from which one can start in search of understanding, are “spinning” in the heating terminal of the battery? There are several of them:
- U – voltage at the terminal.
- I is the current strength passing through the terminal (conductor).
- R – conductor resistance.
- S – cross-sectional area of the conductor.
- t – time.
- Q is the amount of heat dissipated on the conductor.
Let's start with an analysis of the most common error when operating with these quantities and the physical laws by which they are related. It is based on the fact that the terminal heats up due to poor contact, as well as on Ohm's law for a section of the circuit.
The logic is this. The worse the contact, the smaller the cross-sectional area of the conductor S. And the smaller the cross-section, the greater its resistance. Next, we take the above-mentioned Ohm's law:
And this is where the problems begin. The voltage in the car's bot network is always the same, and is approximately 12 V. Almost everyone (many on a subconscious level) understands that the greater the current, the greater the heating. And it is true. But what happens when contact deteriorates? That's right - the resistance R increases. It turns out that the worse the contact, the less current in the circuit should be. How, then, can the terminal heat up due to poor contact? The current is decreasing! It should be the other way around: the contact deteriorates, the resistance increases, the current drops - the heating decreases.
But in practice this does not work, since more than half of the reasons why battery terminals heat up are caused precisely by poor contact. But the catch is that this Ohm’s law cannot be applied to solve this problem. It’s not for nothing that it’s for a section of the chain. And we are far from a site.
Now, if the terminals are short-circuited with a piece of wire, then this law will work. The greater its resistance, the less current will flow, and the terminals will heat up less. And vice versa.
But in the car, in addition to the heating terminal, there are also current consumers - a starter, a stove, an acoustic system, etc. All this also affects the strength of the current flowing through the terminal. But in practice, large currents also flow through poor contacts. And despite the fact that the resistance there has increased, the current strength does not decrease proportionately.
The current still flows. And his strength is great. This can be judged by the fact that the same starter works even with poor contacts. Accordingly, even through a bad contact, a current of more than 100 A flows. That is why Ohm’s law, no matter how cool it is, is not suitable for solving our problem, and the above algorithm will be initially erroneous.
And the correct algorithm will be like this. Since the battery terminal heats up, we are primarily interested in the Q value. It is clear that the larger it is, the stronger the overheating. Let's try to figure out what this Q depends on in the case of a heating terminal. For this, there is a simple formula from a school textbook, which is used to express the Joule-Lenz law:
What does this formula give us? Everything is extremely simple and clear. It tells us that the battery terminal can heat up for several reasons - due to current, resistance or time. The larger these values are, the stronger the heating. Accordingly, in these directions it is worth looking for a possible reason why the battery terminal is heating up.
Possible reason #1. Bad contacts
Let's start with something simpler. Namely, from a bad contact on the battery terminal itself. This happens most often. The terminals oxidize, become dirty, wear out, and the fasteners become loose. The result is always the same - at the junction of the battery and the terminal, the cross-section is reduced. And this leads to increased resistance.
Since current consumers from the battery are able to operate even with poor contact, the current through this section does not decrease. We don't take time into account for now. Let us assume that it does not change, and the starter starts the engine as quickly as with normal contact. We look at the formula and see that in this situation Q increases. The terminal is getting hot.
The problem can be solved very simply. The terminals are cleaned of oxides and securely fixed to the battery. For prevention, it is recommended to lubricate them with special compounds. If there are cracks, deformations or other defects on the terminals, they must be replaced. Cheap, low-quality terminals are not worth buying and installing.
It should be remembered that bad contacts can be not only at the battery terminals. No less often, their overheating is caused by an oxidized, weakened or simply dirty connection of the negative wire to the car body, or the so-called “ground”. In some models it is connected not to the body, but to the engine. In any case, the result of poor contact in this place will lead to overheating of the battery terminals. It is repaired in the same way - oxides and dirt are removed, and the terminal is securely fastened in its place.
The battery terminal gets hot: causes and consequences
The main condition for the uninterrupted operation of any vehicle equipment is reliable connection of all elements with the power supply terminals. When using a large number of high-power consumers, overheating of the battery terminals may occur. An increase in the temperature of the conductive parts of the power source has a detrimental effect on internal processes and can lead to premature failure of the battery. Consider the causes and methods of eliminating possible heating of contacts.
Why does the battery terminal get hot?
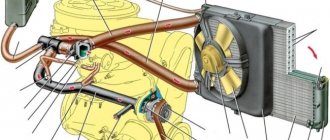
When starting a car, increased currents flow from the battery to the engine and back from the generator to the battery. In winter, the maximum current reading can reach values of up to 600 A. As a result of the use of thin wires not designed for such amperage, overheating of the wires and the terminals themselves is possible.
Important! The positive and negative wires must be designed for the maximum current readings flowing through them.
Many motorists have encountered a problem when the terminal heats up. The main reasons may be:
- Poor connection between terminals and battery terminals. The reason may be either a manufacturing defect or the passage of time. In this situation, it is necessary to notice and correct it in time.
- The appearance of an oxide film. Such troubles can occur relatively rarely, however, it is necessary to ensure the cleanliness of the battery terminals, as well as the inner surface of the contacts.
- Increased resistance of commutating wires. Over time, refraction of the wires may occur, resulting in their gradual rupture. From the physics course, you can recall that as the cross-sectional area decreases, the resistance of the wire increases. In this case, the faulty conductors should be replaced.
- If the negative terminal of the battery heats up, you need to check the connections to the body. Very often, car owners can be confused, believing that the terminal is heating up, but the heating occurs on the wire.
- The positive terminal on the battery is heating up. The reason here can only be if there is poor contact on the tip or oxides have formed that need to be eliminated. In some cases, overheating may occur as a result of a malfunction of the battery terminals themselves.
Danger of heating battery terminals
The very phenomenon of overheating at the battery terminals has a detrimental effect on the performance of the battery. Let's look at a few of the detrimental effects of systematically heating the power supply contact:
- Poor switching may cause the temperature of the battery's internal electrodes to rise. Heating the battery plates leads to intense evaporation of the electrolyte; this phenomenon can lead to premature failure of the power source as a result of the cans drying out and the electrodes falling off. The capacity decreases sharply.
- The constant expansion and contraction of the structural elements of the battery as a result of heating the terminals leads to the appearance of microcracks in the housing from which the electrolyte will subsequently evaporate and leak out.
- If the contact begins to constantly overheat above the melting point of lead, this can lead to deformation of the plates, resulting in a short circuit of the electrodes.
Overheating under load
Overheating can often occur when starting a vehicle. The engine started, we began to apply the load, the contacts began to overheat. This phenomenon can occur due to the inability of the generator to cope with increased loads (modern equipment is equipped with a huge number of different devices and devices to increase comfort), so energy begins to be drawn from the battery. If there is oxide on the terminals, or poor switching, they will heat up.
Advice! When operating a vehicle, it is necessary to control the power consumption of on-board devices in order to avoid overheating of the terminals on the power source.
Ways to eliminate terminal heating
In order to get rid of temperature increases at the terminals, the following rules must be observed:
- Initially, it is necessary to use only working electrical equipment.
- Before installing devices, check the compliance of the rated power value and maximum currents for the given on-board network. If necessary, replace conductors designed for high currents.
- Use a power supply with terminals that match the terminals on the wires. If you purchase a battery with different terminals, it is recommended to replace the terminals on the conductors for normal switching.
- It is necessary to monitor the reliability of connections between wires and lugs. It is recommended to tighten, and in some cases solder, the places where the conductors are switched.
- The surface of the battery terminals and the inner surface of the terminals should be systematically monitored for cracks, chipping and scuffing. If they appear, it is necessary to rub them with zero sandpaper.
If heating of the contacts or wires on the battery occurs, you must first find out the cause and, based on this, carry out proper maintenance of all live parts and surfaces. Proper handling of the conductive parts of the power supply can significantly extend battery life.
batteryzone.ru
Possible reason #2. Insufficient cross-section of power cables
The power wires in a car are considered to be those that go, first of all, to the starter. If they were replaced the day before, then it is likely that in order to save money, cables that were not thick enough were purchased. This means that their resistance is higher than necessary. Accordingly, according to the same formula, heating of the terminal can be observed. Moreover, in this case, the terminal itself may not be a source of heat. Initially, thin power cables overheat, and heat from them is transferred to the terminals.
The solution to the problem is obvious - you need to install cables of sufficient cross-section.
In addition to the wires going to the starter, large currents can flow through other circuits of the car. For example, the same ground wire must also have a sufficient cross-section. If the car has powerful acoustics, an inverter and other “gluttonous” equipment, thick wires are also needed to power them.
The positive or negative terminal on the battery gets hot
Any element of a vehicle can fail. After all, it is not always possible to keep track of everything that happens to the car. In addition, some symptoms are practically invisible unless specifically checked. For example, one of these signals may be heating of the battery terminals.
The positive terminal gets hot
Terminals are the current terminals for batteries. The vehicle's power supply wires are attached to them. They are made of lead.
If the positive contact on the battery heats up, this means that the wire has poor contact with the terminal. This may occur due to oxidation or due to water entering it.
Heating can cause ignition of wiring and a fire under the hood, melt insulation, and damage the battery case.
You can eliminate the causes of heating of the positive terminal as follows.
- Remove the end of the wire from the current terminal.
- Clean the contacts with sandpaper.
- It is advisable to change the wire that goes from the generator to the battery.
- Put the wire back on the terminal and sufficiently tighten the end of the wire that is connected to the current terminal on the battery.
To improve contact, it is necessary to select the desired ring diameter. Then the bolted connection will tightly grip the terminal and prevent this area from sparking and melting.
It is recommended to tighten the bolt nuts with two wrenches. This way you can avoid turning the bolt or nut.
If after cleaning the contacts a few days later a white oxide film of lead has formed again, which leads to poor contact between the wire and the battery, it is recommended to check the battery for electrolyte leakage. The battery may be deteriorating. Cracks have appeared on the battery body through which electrolyte vapors enter.
The negative terminal gets hot
If the negative terminal gets hot, it is due to poor contact with the body. The latter is used in the form of grounding. Oxidation as a result of the release of electrolyte vapors to the outside can also affect.
To eliminate the causes of heating of the negative terminal, it is recommended to do the following:
- Check whether both ends of the wire are connected well enough.
- Clean the terminal from oxides with sandpaper. If oxides still remain, replace the battery with a new one.
Heating of the ground wire from the battery is not in itself dangerous if it occurs due to a poor connection. In case of oxidation and gradual destruction of the battery, this is dangerous for the lives of other components of the car, to which the problem can spread. The heat may cause the body to melt, which will lead to sulfuric acid leaking into the inside of the car.
Both terminals get hot
If both terminals heat up when starting the engine or when turning on the wipers, heated mirrors or seats, this means that the generator cannot cope with the load. Energy is additionally taken from the battery. In case of poor contact, these places become very hot.
To avoid overheating of both terminals when starting up or connecting additional devices, you must repeat all the steps that were described above separately for the negative and positive contacts.
Attention! When working with a battery, you must follow safety precautions and use rubber gloves. If the battery leaks, there is a possibility of damaging exposed skin on your hands.
The wires coming from the battery get hot
It happens that the wire going to the charger gets hot. And the car owner thinks that this is a terminal.
The reasons for cable heating are as follows:
- small cable cross-section, which cannot withstand the load when connecting additional devices;
- break of several threads inside the cable;
- poor cable quality.
All this leads to the fact that the wires will heat up and may ignite. It is recommended to replace the cables with new and high-quality ones. Branded wires have passed European quality standards and have oil-, petrol- and heat-resistant insulation.
Important! It is best to connect the car battery terminals with a braided copper wire.
Conclusion
Poor contact is a signal that the vehicle owner should pay attention to this problem and solve it in a timely manner. This is the only way to avoid the negative consequences that can result from the car owner’s negligence.
istochnikipitaniy.ru
Possible reason #3. Damage to power cables
But what if the power wires in the car are, as they say, “original”, that is, from the factory? In theory, their thickness (section) should be sufficient, and they cannot be the cause of overheating of the terminals. But no. How can they?
The fact is that any power cable consists of a large number of current-carrying wires. This is done to ensure that the conductor not only has low resistance, but is also flexible and durable. But durable does not mean eternal. Due to frequent manipulations with the battery, vibrations, and corrosion, the veins in the power cables are inevitably destroyed. There are fewer and fewer of them over time. Accordingly, the total cross-section of the power cable decreases, and the resistance increases. It starts to heat up and heats up the battery terminal.
In this case, there is only one way out - timely replacement of power cables.
Starting device and general concepts
A starter is nothing more than a starting device. It is he who is responsible for starting the engine. The device is located in the starting system of the power unit, and its purpose is to initially unwind the crank shaft. If the starter is unable to turn the flywheel, starting difficulties begin.
First of all, the starter gives an error if the power supply coming from the battery is insufficient. For this reason, experts recommend starting to test the jump starter with a battery. You need to check whether the battery produces enough current or not. After all, a poorly charged battery cannot power the starter properly.
Testing the battery is carried out in various ways, and the simplest of them is to measure the current using a voltmeter.
It is also important not to forget to test the wiring that makes up the communication between the starter and the battery.
Possible reason #4. The starter "takes over"
When they say “the starter is taking over,” it means that it is drawing more current than usual. Accordingly, the strength of the current flowing through the battery terminals increases. And as the same formula shows, as the current increases, the amount of heat generated also increases. If, at the same time, there are also bad contacts, the engine does not start with a “half-poke” (t increases), then our Q increases in all three directions.
A starter is a rather complex device, and it can “take over” for many reasons. All of them are divided into two large categories - mechanical and electrical. Mechanical causes include all failures that cause resistance to rotation of the starter rotor. Wear of bushings, contamination, jamming, problems with the motor (it is difficult for the starter to turn it) - all this creates mechanical resistance. Because of this, the starter consumes more current to operate.
The second category of reasons is electrical. This includes all breakdowns that cause large current to flow through the starter. Possible wear of the brushes, clogging of the commutator, short circuits in the rotor windings, short circuits to the housing, and so on.
Causes of poor rotation and heating
Not everyone knows why the starter rotates slowly. It turns out that there are reasons for this, and it is not in vain that experienced motorists, when diagnosing the starter, check its performance on a cold and hot engine. Ideally, a car starter should rotate the flywheel well in any condition.
So, the most well-known reason for the starter’s tight rotation and heating during operation is too thick engine lubrication. As you know, the main task of a lubricant is to reduce friction of metal parts of an internal combustion engine. For normal performance of the function, the oil must have a certain temperature. All lubricating oils are manufactured based on this factor.
Obviously, you need to change the oil in a timely manner. If the lubricant life has come to an end, then the oil will no longer be able to perform its useful functions, but will only interfere. This also applies to the starter, which finds it very difficult to rotate an engine filled with thick lubricant.
In addition to the fact that the lubricant must be updated in a timely manner, it must also be selected correctly, according to the time of year. In winter, one type of lubricant should be used, in summer, another.
Oil may become excessively thick due to additives. As you know, today additives are often added to lubricants in order to reduce oil consumption, etc. A large number of additives inside the oil thickens it, which directly affects the operation of the starter negatively.
The second reason for tight rotation and heating of the starter is insufficient battery charge. This has been written about in detail above. You need to check the battery charge, and if it is low and the battery does not hold a charge, find the cause and eliminate it.
The starter may heat up due to wear out of the starter bushings or brushes. The solution suggests itself - disassemble the starter, replace the brushes and bushings. Check how everything works.
The engagement with the flywheel of the crank shaft includes the bendix of the starting device. This is a gear that can also fail for various reasons. The most common is the curvature of the shaft on which the bendix actually sits. As a result, the gear does not completely engage with the flywheel, an extra load is placed on the starter, and it begins to get very hot. Replacing or repairing the bendix and shaft will help solve this problem.
Possible reason #5. Short circuit in wiring
This happens quite rarely, provided that the car's electrical wiring has not been subjected to serious modifications with neglect of safety measures. For example, if you connect any device directly to the battery, disdaining the fuse, then the breakdown of this device can cause a short circuit. With it, the current through the battery terminals will increase significantly (here Ohm’s law will already work), which can lead not only to heating, but also to fire.
Short circuits are also common in circuits that contain fuses. Often, after they fail, they are replaced with new ones with a higher denomination. As a result, they do not respond in a timely manner, which leads to serious problems.
Damaged insulation, careless twisting, excess moisture - all this can also cause a short circuit. In this case, there will not necessarily be a characteristic smell and smoke, but the heating of the battery terminals can be very noticeable.
Possible reason #6. Large and long-term load on the battery
Quite often, the battery terminals heat up when it is used for a long time while parked to power powerful consumers. This could be multi-watt acoustics, a refrigerator, or an inverter. Today in a car you can turn on almost anything, even a kettle and a boiler. What does this mean?
When the engine is not running, absolutely all the electricity consumed is taken from the battery. If a powerful device is turned on, the current it consumes directly depends on the power. And if we take into account that it works for a long time, then the Q discussed above will grow in two directions at once. A third direction will inevitably also be added if a powerful device is connected with thin wires that are poorly screwed, oxidized, rotten, and so on.
To fully understand this point, let’s briefly consider what does it mean – a large load on the battery? It can be calculated and compared with the parameters recommended by the manufacturer. So here it is. Any car battery will serve long and reliably if it is not discharged for a long time with currents exceeding 1/10 of its capacity.
This means that for a battery with a capacity of 60 A*h, “harmless” discharge currents do not go beyond 6 A. How can you find out how many amperes the battery supplies to power a particular device? By its power. For example, when you went out into nature, you turned on a speaker system with a power of only 150 W. To find out the current strength, you need to divide this power by the voltage, which in this case is approximately 12 V. It turns out that such music takes a current of about 12 A from the battery. Accordingly, with a 60 A*h battery, the load on it will exceed the recommended one by two times. Heating of the terminals is ensured.