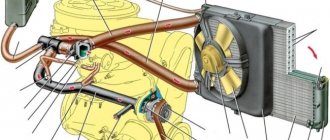
VAZ 2109: engine overheating and the reasons for it
VAZ 2109 engine and its overheating
It is no secret that the cooling system of domestic cars of the VAZ family is in most cases far from ideal. On the VAZ 2109, engine overheating is a common flaw that leads to complex consequences. On the VAZ 2109, the engine overheats more often due to the human factor, but there are other reasons. We will talk about them in this article.
Causes of the defect
There are several reasons for engine overheating on VAZ models. One of the most common is reducing the amount of coolant to a level below the minimum permissible. This occurs when there are leaks at the joints, as evidenced by stains in the engine compartment.
Radiator clogged with dust
The next reason for engine overheating on the VAZ 2109 is the injector. The liquid circulates through it in a limited volume and does not have time to cool. A stuck temperature sensor causes the fan to turn on late, which is another reason that the engine cooling fluid does not have time to cool before the next cycle of passage through the motor circuit.
Loosening of the drive belt on the fan, if it is connected to the engine shaft, due to an oversight on the part of the driver, leads to its unstable operation and it does not provide sufficient airflow to the radiator.
Common causes of VAZ 2109 engine overheating
It is worth noting that engine overheating is a big problem. Everyone knows that a car’s power unit consists of many parts and assemblies that are very sensitive to temperature conditions. These include oil seals, piston rings, and other equally important parts. Under the influence of high temperature, which is formed during overheating, oil removal ring expanders lose their elasticity, as a result of which the engine begins to consume more oil than before.
Note. But this is only the tip of the iceberg, because according to the law of physics, all this inevitably leads to the expansion of bodies. During overheating, engine parts become deformed so that they can no longer be restored. In particular, the cylinder head warps, the pistons become deformed, and the block itself fails.
Thermostat
VAZ 21093 engine overheating
As mentioned above, there may be several reasons for engine overheating. The thermostat is one of the reasons. How does engine operation affect the functioning of the thermostat:
- The cooling system consists of large and small circles through which coolant circulates.
- The antifreeze moves in a small circle when the engine is still cold.
- When the engine heats up, the coolant begins to circulate in a large circle (the thermostat opens, which circulates the antifreeze in exactly this way - through the radiator).
- If the thermostat does not function well or fails, then the liquid circulates in a small circle without passing through the radiator. This leads to engine overheating.
Checking the Thermostat
It is easy to check the operation of the thermostat:
- Warm up the engine to 90 degrees Celsius.
- We feel with our hands the pipe going to the radiator. If it is not heated, then the thermostat is not functioning.
Replacing the thermostat
In order to replace the thermostat it is enough:
- Drain the coolant.
- Loosen the clamps.
- Remove the pipes.
- Clean off old sealant.
- Install a new thermostat and secure it with a new layer of sealant.
- After the sealant has dried, put on the pipes.
Fan switch sensor
VAZ 2109 engine overheats
Often, on a VAZ 2109 car, this particular sensor for turning on the cooling fan does not work.
Note. This problem is not observed on older modifications of the VAZ 2109, where the fan runs directly from the motor. On the latest versions of the VAZ 2109, this problem is relevant. Operating principle of DVV
- Two wires come out of the sensor, the closure of which leads to the connection of the fan.
- DVV connects the fan at the moment when the radiator overheats above 80-90 degrees Celsius.
Correcting the situation
It will help you do the following:
- Or short-circuit the sensor wires yourself.
- Or check the fuses.
- Or replace the sensor.
VAZ 2109 engine overheated
Air lock in the radiator
Another common cause of engine overheating. In other words, this is a layer of air that forms in the radiator due to the difference in density of liquid and air. The plug will remain in one place and prevent the antifreeze from moving through the pipes.
Checking for air lock
It's easy to do:
- We warm up the radiator.
- Check to see if it's all hot. If not, it means in a place where the temperature is different and there is an air lock.
Solution
The engine of a VAZ 2109 overheated
- We press on the upper pipe going to the radiator (we pump, as if pumping a hose).
- We do the same with the remaining pipes, provided that the antifreeze (see Replacing antifreeze - the subtleties of the process) is completely filled.
- We pump until bubbles stop appearing in the expansion tank.
Coolant leak
Another reason why the VAZ 2109 engine overheats. Caused by the following components:
- The pipe leaked over time. The solution is to replace the hose or, if it happened on the road, wrap it with tape or tape.
- The thermostat or radiator has failed. The solution is to top up the antifreeze and drive to a nearby service point or store. Then replace the part.
Cylinder head gasket
VAZ 2109 engine boiled
The most common and frequent cause, which is not immediately identified. The fact is that the coolant level begins to decrease gradually, not immediately. An external examination reveals nothing. It turns out that the cylinder head gasket allows fluid to pass through the oil passages into the oil pan. To make sure of this, you need:
- remove the oil dipstick;
- pay attention to the color of the oil.
Note. If the color of the oil is cloudy, slightly coffee-colored, then it contains elements of antifreeze. Replacing the gasket
- The throttle wires and cables are disconnected from the carburetor.
- In addition, the choke cable is dismantled.
- Rubber hoses and pipes are removed.
- The distributor is also removed.
- The three bolts securing the distributor to the cylinder head are unscrewed.
- Liquid is drained.
- The remaining parts that interfere with removing the cover are dismantled.
- The cover itself is secured with two cork nuts.
- They are removed, then the head is dismantled.
- Finally the gasket, which is replaced with a new one.
The above replacement instructions are not complete, but they give the reader a general idea of the operation. The DIY work described above to eliminate the causes of engine overheating is practical information that can be applied in practice. During the work process, it is recommended to use photo and video materials. We remember that it is better to eliminate the cause of overheating in a timely manner by spending a certain part of the money on new parts, rather than later paying double the price for major repairs.
Source: masteravaza.ru
5.1.10 Engine overheating
When the engine is running, a properly functioning cooling system maintains optimal temperature conditions. Malfunctions in the cooling system can lead to engine overheating. If you miss this moment, unpleasant consequences may arise: breakdown of the head gasket, warping of the head and, as a result, complex engine repair. There is a coolant temperature gauge on the dashboard of any car. If the engine overheats, the gauge needle approaches the red zone. Unfortunately, we do not always pay attention to this device in time and realize that the engine is overheating only when we notice steam emerging from under the hood or even hear its whistle.
Checking the cooling system
At the first signs of overheating, if the temperature gauge needle has moved into the red zone, but no clouds of steam are escaping from under the hood, fully open the heater valve and the air flow control air damper, and turn on the heater electric motor at maximum speed.
Turn on the hazard lights, depress the clutch pedal and, using the inertia of the car, try to carefully move to the edge of the roadway and stop as far to the right as possible on the side of the road, and if possible, outside the roadway. Let the engine run for a couple of minutes at normal idle speed with the heater on full blast.
Warning
Do not stop the engine immediately! The only condition is to maintain the tightness of the cooling system. If the hose bursts or comes off, or another leak occurs other than fluid knocking out from under the expansion tank plug, the engine will have to be stopped immediately!
After stopping the overheated engine, local overheating of the coolant begins at the points of contact with the most heat-stressed engine parts and the formation of vapor locks. This phenomenon is called “heat stroke”.
Stop the engine. Please note that an overheated engine cannot stop immediately after turning off the ignition and continues to operate due to the so-called pseudo-ignition. Such work is harmful to the engine, so you should stop it forcibly, either by smoothly pressing the gas pedal to the floor, or by engaging any gear with the clutch depressed, and then pressing the brake and releasing the clutch.
| EXECUTION ORDER |
Lada 2109 Ap-ak › Logbook › The engine will no longer overheat! Let's learn the intricacies of thermoregulation VAZ.
Hi all!
Today we will talk about the most common causes of chisel motor overheating.
I will talk about my experience in repairing and operating a car, so there will be no stupid copying of text in this post. Please do not judge strictly, because... I'm not a professional auto mechanic! The main causes of overheating:
1) The most common reason is a non-working coolant fan
.
I think everyone is familiar with the principle of operation of the coolant fan - it forcibly cools the engine. It may not work for several reasons: 1.1 The coolant temperature sensor is not working. 1.2 No power to the coolant sensor 1.3 The coolant fan itself does not work
CHECKING THE TEMPERATURE SENSOR
So, if you see that the cause of engine overheating is the coolant fan not turning on, the first thing you need to do is check whether it is receiving power.
Now turn on the ignition! For carburetor
models 2109, the coolant sensor is located on the radiator.
There are 2 wires coming to it and in order to check if there is power on them, simply short them. Don't be alarmed, it's the fan that turned on :)! If it does not turn on, then see the following points. On the injector,
the sensor is located next to the thermostat, under the air filter.
It also comes with 2 wires, but here, unlike the carburetor, you don’t need to short-circuit the wires with each other, you just need to pull out the block and the coolant fan will turn on. If after these steps the fan does not turn on, there are two reasons: No power; There is power, but the fan does not work. To finally make sure there is power, you need to ring the contacts with a multimeter or test lamp. If there is no power, then first of all we look at the fuse, and since the +
of the coolant sensor sits on the same fuse with the signal, it’s enough to just press the horn, but even the horn may not work
IT’S THE SAME FUCKING VAZ :):)
Just look at the fuse if it is intact, we follow the diagram and look at all the contacts.
If there is power, then we simply connect the fan directly to the plus
and
minus
of the battery - now it should turn on, didn’t it turn on? This means we need to replace the fan, or try to repair it :)
Main causes of overheating
ATTENTION! A completely simple way to reduce fuel consumption has been found! Don't believe me? An auto mechanic with 15 years of experience also didn’t believe it until he tried it. And now he saves 35,000 rubles a year on gasoline! Read more"
Most likely, if there are no characteristic reasons for overheating, the pump has simply outlived its useful life. Simply replacing it can completely eliminate the problem. On the other hand, if the cause is not eliminated, the new pump will also heat up like the old one, and the money spent on the purchase can be considered lost.
However, this rarely happens. More often than not, problems are actually related to the pump.
Here are the main causes of overheating.
- Dirt. A device used for a long time will overheat faster. It is necessary to check all pump elements, including the filter mesh. Clean or replace consumables if necessary.
- External damage, such as a crack or something similar. The cause may also be wear of the device’s gears or rollers protected by hydraulic superchargers.
- Driving with Chek-Engin. Some motorists ignore the warnings that the car sends. They continue to drive, although the system notifies that there are problems, including those related to the fuel pump.
- Driving with a red light. It lights up on the instrument panel if the volume of fuel liquid in the tank is critically small. It is especially dangerous to travel with a half-empty tank in hot weather. The fuel pump will soon overheat.
- Refueling at questionable gas stations. Pumping low-quality fuel also negatively affects the operation of the pump. If the fuel contains a large amount of sulfur, the commutator will gradually become covered with a dark coating, contact with the brushes will deteriorate, and sparking will begin inside the device, which will lead to overheating.
- The main filter is clogged. This is a separate part installed in the section of the fuel line. It has the ability to retain small particles of debris that get into gasoline.
- Violations in the voltage circuit, short circuits. This is also a clear reason for overheating of a modern type electric pump. With such problems, the pump begins to turn on in starting mode, and as a result overheats.
Engine overheating on a VAZ-2109 car - possible causes and ways to eliminate them
The cooling system on the “nines” is far from ideal - any owner of this car will readily confirm this. Accordingly, engine overheating is a fairly common cause. In fact, the root causes here can be divided into 2 main groups:
- human factor;
- technical difficulites.
With the first one, everything is probably clear. That is, in this case, the occurrence of the problem is explained by the incorrect actions of the car owner. An example here is the use of various additives that are added to the oil. If used incorrectly, they leave a deposit on the cylinder walls, which, in turn, provokes problems in the operation of the cooling system. Therefore, it is better to avoid additives altogether and just use high-quality oil.
Also, many owners of “nines” believe that plain water can be poured into the cooling system of this car, although antifreeze today is not that expensive. Because of this, plaque appears on the tubes and walls, which causes problems with normal engine cooling.
It often happens that the channels are completely clogged. Naturally, in such a situation, the coolant simply cannot get into the engine, and overheating of the power plant in this case is a matter of time.
Another possible reason is long-term operation of the engine in extreme conditions. Often, owners of “nines” overestimate the capabilities of their car’s power plants and, as they say, turn them all the way up. Because of this, the cooling system cannot fully cope with its responsibilities. Overheating of the engine will be a completely natural result in such a situation.
Drivers should also monitor the coolant level. If it is not enough, then engine overheating is inevitable, the only question is when it will happen. However, in fairness, it is worth noting that it is often very difficult to identify leaks in the system. Meanwhile, even the smallest hole is enough for antifreeze to escape. The tank can be completely empty after just a few tens of kilometers. Therefore, even if you check the level before the trip, this will not prevent breakdown. By the way, the most dangerous leak is when coolant gets into the oil or directly into the combustion chamber. The consequences in this case will be very serious - water hammer.
However, reasons of a purely technical nature are much more common. For example, old engines with a mileage of over 200 thousand, both injection and carburetor ones, have a problem such as the accumulation of deposits inside the combustion chamber, which appeared due to excess oil. The latter, as you know, does not burn very well. Because of this, plaque appears on the walls of the combustion chamber, the volume of which gradually increases. As a result, such an undesirable phenomenon as overheating is provoked, and in this situation the temperature sensor does not give any “alarm signal”. You can guess that this is the problem by the color of the exhaust - it turns gray.
Thermostat failure is another technical reason. The circulation of coolant through the large and small circuits depends on the operation of this unit. If the thermostat fails, the coolant may begin to circulate in only one of them. You can understand this by how the engine heats up. In particular, if the liquid flows only in a large circle, then in winter the engine will have difficulty warming up to operating temperature, and if it is too low, the power plant will overheat.
Causes of overheating
All possible causes of overheating of the power unit of a VAZ 2109 car, as well as other cars, can be divided into two categories:
- External reasons;
- Internal reasons.
As you know, domestic nines are equipped with injectors and carburetors. Therefore, we will get acquainted with all the likely situations that can lead to overheating of one or another type of engine.
External
Let's start with the external reasons for the increase in engine temperature.
Causes
Features of the situation
Low coolant level
Quite often the engine overheats due to a low level of coolant in the expansion tank. It is not always possible to immediately detect a leak in the system. Antifreeze requires a very small hole in order for it to completely drain out of the tank over several tens of kilometers. The most dangerous leak is coolant entering the combustion chamber or oil, which leads to water hammer
If your engine begins to overheat, pay attention to the condition of the thermostat. This unit controls the movement of coolant along a large or small circuit. If the thermostat breaks down, the coolant stops moving in a large or small circle. In the first case, the engine will have difficulty warming up to operating temperature in winter, and in the second, the engine will constantly overheat
Radiator clogged, ineffective cooling
If almost the main component of the cooling system, that is, the radiator, becomes dirty, overheating will not be avoided. If there is dirt on the radiator fins or its “honeycombs,” heat transfer is significantly reduced. Plus, pay attention to the performance of the fan. It may not work due to belt tension, a broken temperature sensor, or a failed fan motor.
Long-term operation in unacceptable conditions
Often the cause of increased engine temperature is the driver himself, who overestimates the capabilities of his car and operates it in conditions that are contraindicated for it. These include prolonged idling, improper slipping, increased speed - all these situations negatively affect the condition of the engine, since the cooling system does not have time to perform its functions.
Engine operation under detonation conditions
If the driver ignores the appearance of detonation in the cylinders, the engine cooling system will not be able to cope with the load. Add to this the hot weather, and then you won’t envy the engine
Exhaust valve burnout
If the exhaust valve fails, the gases heated to an impressive temperature will overheat the engine. The situation can only be corrected by repairing the power unit
Water pump problems
If the water pump fails or stops working properly, coolant will not be able to circulate through the system. Pump failure may be due to tension in the drive belt, defective pump blades, or breakdown of the pump itself.
Thermostat
Internal reasons
There are several reasons that contribute to internal engine overheating.
Causes
Peculiarities
Accumulation of deposits inside the combustion chamber
This is a typical problem for old VAZ 2109 carburetor and injection engines, which have driven more than 200-300 thousand kilometers. Excess oil forms in the combustion chamber. Oil burns poorly, causing plaque to accumulate on the walls. This leads to overheating, which the temperature sensor cannot report. The malfunction can be determined by the bluish smoke protruding from the exhaust pipe. Or the impaired performance of the motor will indicate this
Plaque in the cooling radiator
The mistake of many owners of domestic cars is that they consider it sufficient to pour plain water into the cooling system, replacing the not-so-expensive antifreeze with it. But due to contamination of the water or the use of low-quality coolant, plaque forms on the walls and tubes, preventing normal cooling of the engine. It is not uncommon that the channels are simply blocked by plaque, which leads to impaired access of coolant to them. Overheating is only a matter of time in such a situation
Additives in oil
We don’t know how to explain the desire to add all kinds of additives to the oil. But if you do this and don’t know why these additives are actually needed, an impressive coating will form on the cylinder walls, due to which a violation of the efficiency of the cooling system cannot be avoided
Lada 2109 Doll › Logbook › Reaching maximum power, or what is the reason for engine overheating
With the onset of summer, the days became hot, and standing in city traffic jams became simply unbearable. At these moments, most drivers begin to blame themselves for the fact that when buying their car they saved a little and did not install air conditioning - now they have to survive on their own sweat in the cage of a personal vehicle. However, not only people feel the summer “smokehouse”: car engines endure much greater temperature loads than we do.
Engine overheating on modern cars is not as pronounced as, say, on Soviet-designed cars. Judging by the number of installed “fan buttons,” engines of the “Samara” and “Samara-2” families, as well as cars of the “Tenth” family, are prone to overheating. Are the engines of domestic front-wheel drive cars really prone to overheating? If so, where do the roots of this problem come from? Is it a defect of the motor mechanics and designers of the Togliatti plant, or are we operating the machine incorrectly? And why is there no such problem on Zhiguli cars? I propose to dot all the E’s, and for this we need to compare two engines: “penny” and “eight”...
The penny engine was developed in the late sixties by FIAT. The upper position of the camshaft made it possible to increase the maximum engine speed, and as a result increase the efficiency, elasticity of the unit and maximum power. Since the cooling fan was forced to rotate from a belt, and the degree of engine cooling was highly dependent on the crankshaft speed, it was decided to install a high-performance pump for better fluid circulation and use a copper radiator. Oddly enough, in hot traffic jams the engine is still prone to slight overheating. In further classic engines, an electric fan was installed, which made it possible to cool the engine with a much larger displacement without any problems. Well, now let's move on to a more progressive design...
An engine for a front-wheel drive car must have a number of design features: firstly, it must be as short as possible so that it and the gearbox can easily fit between the wheels, and secondly, in order to achieve fuel efficiency, the engine must run on ultra-lean mixtures and have higher efficiency, which requires a higher compression ratio. These two factors determined the design of the VAZ 2108 engine, developed jointly with Porsche. More than 500 different configurations were worked out, and the result was the most reliable automobile engine ever created in the USSR. To reduce the weight of the front part of the car (and to reduce the cost of the car as a whole), the radiator material became aluminum, and the pump was half as efficient, which negatively affected heat transfer. However, the presence of a powerful electric cooling fan compensated for this shortcoming. The resulting 1.3-liter engine produced 64 hp. (47 kW). The piston diameter was 76 mm and its stroke was 71 mm. The distance between the cylinder axes was 89 mm. Then VAZ’s independent development of a more powerful one and a half liter engine began. The whole difficulty of the development was that while maintaining the same engine dimensions, it was necessary to increase its volume. The only way to do this is to increase the piston diameter to 82 mm with the same inter-cylinder distance. It became structurally impossible to leave ducts between the cylinders and, as a result, the more loaded engine got rid of the water jacket between the cylinders, which clearly did not improve the temperature stability of the engine.
Oddly enough, in the entire model range of Lada engines, starting from 1.2 to 1.7 liters, fluid flows were preserved - there the inter-cylinder distances were initially quite large, which made it possible to increase the engine volume without any problems. Theory is a theory, but how the absence of ducts affected the engine temperature will be the main topic of today’s article. For a visual calculation, we launch the design program and recreate a three-dimensional model of the standard VAZ 2108 engine based on its dimensions. An ideal copy of the engine would require several weeks of work, so we will recreate only those elements that we really need.
To understand the processes of heat exchange in the engine, there is no need for the complex shape of the ducts in the cylinder head, and therefore we simplify it, thereby relieving the computer of painfully long calculations. We fill the internal cavity with water and add a pump capacity of 1 l/sec, which corresponds to performance at a crankshaft speed of 4000 rpm. Let the temperature at the engine inlet be 75 degrees; let’s create an imitation of engine operation under moderately loaded conditions. Next, we add the heat generation power and start the calculation. The first thing we get is a cross-sectional picture of the engine: here you can clearly see which cylinders heat up to what extent.
As you can see, the last cylinder from the pump (fourth) heated up the most - its temperature was 168 degrees Celsius. We launch weightless balls into the cavity and watch how the liquid covers the cylinders. The color of the balls also indicates the temperature of the water.