Why, after repairing the engine, does it consume oil?
The first and main reason is the absence of a so-called “mirror” on the cylinder walls. Overhaul involves processing (and possibly boring) cylinder head liners. After which the so-called honing. Microscopic scratches are applied to the walls in a certain order. During the running-in process, these risks are polished, ensuring perfect tightness (and as a result, good compression).
However, honing is the reason why oil consumption increased after engine overhaul. Possible incorrect orientation of the rings, or other errors by repairmen. But most often the reason is in the honing. Usually after 1000-2000 km the problem disappears. If oil consumption has not decreased after engine overhaul and running-in, it is necessary to remove the cylinder head and measure the liners for geometry.
Another possibility is a problem with the valves. Valve seals and poor-quality processing of the neck can also contribute to this.
Many car owners, not understanding why the engine is burning oil after repairs, immediately try to repeat the investment. And sometimes it’s enough just to check the gaskets and seals for leaks.
Changing the oil after engine overhaul
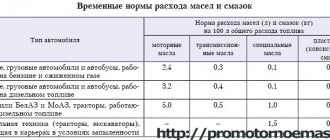
Lubricants are changed more often than usual during break-in. And, of course, along with the filter. Metal shavings and wear debris are bound by oil and must be removed from the engine crankcase. Since repeated oil changes after engine overhaul are expensive, I want to save money on the manufacturer. You can use the recommended brands, or limit yourself to the tolerances established by the car manufacturer. The main thing is not to experiment with viscosity .
There are also special break-in oils. They contain special additives that wash out wear products and do not clog oil channels. But the repair instructions for your car prescribe certain brands of repair oils. And they must be strictly adhered to.
For what reasons does the engine consume oil, what to do
Almost every driver faces the problem of burning oil in the engine. This situation can be caused by many reasons. Only after diagnosing the engine can the cause of the high consumption be determined.
If the engine is new or has undergone a major overhaul, then the norm is a consumption of 20-40 grams per thousand kilometers. If the conditions in which the car is operated are difficult (mountainous terrain, sudden and frequent acceleration), then the consumption can reach 100 - 200 grams per thousand. But when oil consumption is measured in large quantities, you can be sure that something is wrong with the engine.
Engine Toyota 1NZ FE
The 1NZFE is a four-cylinder in-line engine. It has a VVTi type variable valve timing system on the intake camshaft. However, after modernization, the manufacturer installed hydraulic compensators on the 1NZFE. Now car owners do not need to visit a service station after every 30 thousand kilometers to adjust the valves.
This series is still in production today. It is installed on 17 modifications of Toyota vehicles. It is a reliable engine with a mileage of up to 700 thousand kilometers with proper care and annual service.
Attention! 1NZFE, unlike the ZZ series, after a run of 150 thousand kilometers, they begin to actively absorb lubricant. This happens because the oil scraper rings are coked. You may have to replace them and the caps.
The following problems often appear on 1NZFE due to the fault of car owners:
- The oil pressure sensor fails;
- The rear crankshaft oil seal is leaking;
- The cylinder block wears out after a mileage of 200 thousand kilometers.
This happens because they poured low-quality oil not recommended by the manufacturer. A mismatch in viscosity leads to overheating and friction of 1NZFE metal parts.
In addition, these Japanese engines are not subject to major repairs from the first moment of their appearance. Therefore, experienced mechanics recommend pouring only branded lubricant or its analogues.
For what reasons does the engine eat more oil than it should?
To understand why the engine began to consume more oil, you need to study the factors leading to this situation.
Engine overheating
One of the reasons for increased engine oil consumption is too high a temperature in the cylinders. This happens when the ignition timing is broken; if we are talking about a diesel engine, then the fuel is injected at the wrong time. If you use gasoline that is not intended for a particular engine, the temperature will also become too high due to detonation.
If the engine overheats, the oil seals are damaged and scuff marks appear on the cylinder walls. Often one incident of overheating is not enough to cause damage. Of course, if this did not last long and the coolant was not brought to a boil.
Usually, even a couple of such cases pass without harm to the motor. But with several overheats, the material of the caps becomes rough. The required contact between them and the valves is not ensured. The result is that oil appears in the intake manifold. Then it enters the cylinders, and smoke can be seen in the exhaust gases.
Using oils that are not suitable for viscosity
Cuffs may lose their original properties if incorrectly selected additives are used. Oil consumption will also be increased in the case when, instead of the one provided for a particular car, the first available one is filled.
It’s good if it matches the required viscosity, or the parameters are close to it. If this is not the case, then increased consumption cannot be avoided.
Engines that were developed in the 80s were designed to operate with viscous mineral water; as a result, thinner synthetic compounds cause leaks.
Among other things, a unit designed for mineral oil begins to smoke when filled with synthetic oil. Modern engines run on synthetics, and the use of mineral compounds will lead to oil getting into the combustion chamber and repairs even after a relatively short mileage.
Wear of rings, valve stem seals
The next reason for increased oil consumption is wear of the piston rings or oil seals, or both. In such cases, the oil ends up in the combustion chamber, as evidenced by the smoke in the exhaust gases.
Methods for running in the engine
You can properly run in the assembled engine after a major overhaul using stands or during operation. At the service station, engine testing takes place in 3 stages:
- cold running;
- hot running without load;
- hot running with load.
The stands allow you not only to run in the engine, but also to check the quality of repairs. To do this, during the test the following is monitored:
- oil and coolant temperature;
- line pressure;
- crankshaft speed;
- developed power;
- specific fuel consumption.
Run-in is considered complete when the parameters reach a certain range of values and the engine is operating properly:
- at idle speed and at maximum shaft speed;
- evenly in all modes, without sudden knocks and noise;
- there are no oil, fuel or coolant leaks through the connections.
Let's take a closer look at how internal combustion engines are tested in service stations and in garage conditions. The methods are equally suitable for both gasoline and diesel engines.
Run-in on the stand
The stands are suitable for both cold and hot running. The equipment is an installation with an electric motor, control and measuring devices and a cardan shaft for transmitting rotation. The equipment is controlled automatically according to a given program.
The stand is selected according to the engine power. After a major overhaul, the motor is mounted on the unit, lubricant and coolant are added, and the necessary pipes and electrical connectors are connected. The test is completed by inspecting the internal combustion engine:
- remove the pallet;
- inspect the main bearing shells and crankshaft journals;
- If necessary, remove the cylinder head and remove the pistons.
Cold running, unlike hot running, is performed at low speeds of the electric motor, not the motor. The test lasts 20 - 40 minutes with a gradual increase in the rotation speed of the electric motor. During the process they control:
- heating the area where the cylinders and main bearings are located by checking by touch;
- tightness of connections;
- uniformity of engine noise;
- oil pressure and temperature.
Similar article Timing marks for 406 ZMZ engine
For example, KamAZ-740 engines are tested according to the following scheme:
| Crankshaft speed, rpm | Mode time, min |
| 600 — 800 | 20 |
| 1000 — 1200 | 15 |
| 1300 — 1400 | 5 |
To reduce the inspection time by 2 times, low-viscosity oils and special additives are added to the internal combustion engine. This technological technique also makes it possible to reduce metal removal from running-in.
Benchless cold running
This option of cold engine running after overhaul is outdated. The car is attached to a tow rope and pulled in 3rd gear for several hours. This method does not allow tracking individual motor parameters and monitoring its condition.
Hot running
Hot running is the most popular method of testing a overhauled engine. It is carried out on a stand or on a machine with or without a load. Before testing on the stand, spark plugs are installed on the engine, the timing gaps are adjusted, and the power and fuel supply systems are connected. Running in the internal combustion engine is accomplished by rotating the crankshaft, so it is important to monitor the parameters of technical fluids.
During hot running without load, the internal combustion engine is started at a reduced crankshaft speed of 800 - 1100 rpm with a smooth increase in speed. The process takes from 20 minutes to several hours and is completed when half the nominal shaft speed is reached.
For example, the mode for engines ZMZ-405, 406 and 409 is as follows:
| Crankshaft speed, rpm | Mode time, min |
| 850 — 1000 | 5 |
| 1400 — 1600 | 5 |
| 1800 — 2000 | 5 |
| 2300 — 2500 | 5 |
The ZIL-645 test is carried out in 8 stages:
| Crankshaft speed, rpm | Mode time, min |
| 1400 | 10 |
| 1500 | 5 |
| 1800 | 5 |
| 2000 | 10 |
| 2200 | 10 |
| 2400 | 10 |
| 2600 | 5 |
| 2800 | 5 |
For running-in under load, the driveshaft of the stand is connected to the flywheel of the internal combustion engine. The electric motor will act as a generator and load the motor at the same time. The test is carried out with a gradual increase in electric motor power and crankshaft speed in accordance with the technical documentation.
For example, YaMZ-238 is checked according to the following scheme:
| Crankshaft speed, rpm | Load, kW | Mode time, min |
| 1500 | 10 | |
| 1600 | 29 | 10 |
| 1700 | 59 | 10 |
| 1800 | 88 | 5 |
| 1900 | 118 | 5 |
| 2000 | 147 | 5 |
Natural engine running-in
Natural or operational running-in is done without a stand and lasts for 2000 - 3000 km. To properly break in the engine after a major overhaul, you must follow the following rules:
- do not pull trailers, avoid slipping;
- keep the motor in the rotation range of 1500 - 4000 rpm;
- do not coast.
Similar article Setting timing marks for Priora engine 16 valves VAZ 21126
Operational running-in of the engine involves a gradual increase in load:
- for the first 1000 km it is necessary to keep the speed to 3000 min-1;
- increase the next 1000 km to 3500 min-1;
- after 2000 km - up to 4000 rpm.
It is permissible to give a constant load to the engine after 5000 - 8000 km after repair.
Why is it necessary to run in an engine after a major overhaul?
Running in an internal combustion engine is necessary in several cases - after leaving the factory, after half a year of repairs, or after a long period of inactivity. Moreover, you should consider that a factory engine is always faster to run in than a repaired one. Even perfectly fitted parts cannot be so smooth that you can drive at full speed on the first trips.
Read
It is important to realize that engine overhaul involves the introduction of machined parts, which are impossible to fit together with 100% quality. Therefore, they need long-term running-in, during which the mechanism will achieve complete harmony. In general, running-in takes about 3000-5000 km in summer, and up to 6000-7000 in winter. In general, this depends on the type of repair, the fuel and lubricants used, the roads and the skill of the driver.
Duration and features of engine running-in after capitalization
The most important period for a rebuilt engine is the first three thousand kilometers. During this period, it is extremely important to strictly follow the recommended driving regime, especially until the vehicle reaches a thousand kilometers. We list the general rules for running in:
- Driving at high speeds is unacceptable; driving at lower speeds than the nominal speed is also undesirable,
- a gentle driving mode does not mean that you should move at a constant speed and speed - the driving rhythm needs to be changed, but within acceptable limits,
- It is highly undesirable to load the car for the break-in period, much less use a trailer,
- You should avoid sudden acceleration/braking and completely abandon the habit of engine braking.
Strictly speaking, running-in does not allow even short-term operation of the engine in heavy conditions. You should always start with very moderate loads, gradually increasing them. Long-term operation at idle is undesirable (only to warm up the power unit), since idling for a car is also considered a difficult and difficult mode.
As with a new car, the engine oil should be changed after driving the first thousand kilometers. In this case, engine flushing is unacceptable, as is the use of all kinds of additives and additives.
Let's consider the features of running in the power unit, depending on the scope of work carried out as part of a major overhaul. Recovery can be complete or partial. A complete reconstruction of the engine assumes that work has been carried out affecting all the main engine systems: CPG, crankshaft, timing belt. In this case, the recommended run-in mileage is at least 3,000 kilometers. Partial repairs involve the replacement and restoration of individual engine components (piston rings, camshaft, valves), and in most cases, to grind in the parts, it is enough to drive a thousand kilometers in a gentle mode.
Since a complete “capital” is more common, we provide recommendations for running-in specifically for this case:
- before setting off on the road, you should warm up the power unit at idle, but not for too long (we already said that this is harmful) - it will warm up to operating temperature while driving,
- It is advisable to plan your route in such a way as to minimize travel on steep slopes. During the run-in period, passengers are not allowed to be in the cabin.
- engine braking, quick acceleration and emergency braking are unacceptable,
- The recommended driving speed is 60 km/h, regardless of the type and power of the engine. In this case, the speed should be kept below 2500 rpm and dropped for a long time below 1500 rpm. Beware of the operation of the power unit in tension,
- A common mistake is the desire to drive in one gear, maintaining a constant speed. The dosage of load on the motor should be smooth, deceleration/acceleration should be present, but the speed should always correspond to the selected gear. In this case, the engine operates at average speed for this mode.
Moderate driving in all senses during break-in provides the piston rings with the opportunity to settle, settle more comfortably in their places - the piston grooves, the surface of the cylinders gradually acquires a mirror cleanliness, etc. That is, real driving allows you to smooth out all those inaccuracies that cannot be eliminated during grinding, even with the most modern equipment.
We also note that the specified break-in period of 3,000 kilometers is considered the minimum required for a complete overhaul, while complete grinding in of the moving elements of modern internal combustion engines occurs after driving 7,000-10,000 kilometers. In other words, the light running-in mode should last much longer. Maximum loads are permissible only after the above segment.
Running in the engine after overhaul - VAZ and other cars
Before you start running in, you need to perform a number of simple but necessary steps.
If you previously deviated from the advice of manufacturers and used cheaper oil , then during break-in you should return to those recommended specifically for your car brand. It is important to check that oil enters the engine components within 3-5 seconds, since “oil starvation” is unacceptable. It is important to check the oil pressure level at idle speed; it varies depending on the type of engine between 0.5 - 1.0 atm.
- Preliminary work
- first, we wash and blow out the intercooler;
- then we replace the air filter, or at least the oil in it;
- change oil and fuel filters;
- We change the oil in the engine and check its level;
- pay attention to the coolant ;
- refuel the vehicle sufficiently;
- adjust the injectors, fuel pump, regulator;
- remove air from the fuel system. (we check the lambda probe)
First launch after major overhaul
The first start of the internal combustion engine is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Fill in engine oil. It will take 10 minutes for the lubricant to fill the system. The oil filter is left dry to avoid air lock.
- Connect the fuel pump or supply fuel manually.
- Open the throttle manually if there is no automatic drive.
- Start the starter.
- Spin the motor up to 2000 rpm.
- Leave to idle for 15 minutes until engine rotation becomes stable at operating temperature.
- Turn off the unit and wait for it to cool completely.
Similar article Markers for setting the ignition on the 405 ZMZ timing engine
During startup, the pressure in the lubrication system is monitored. The indicator signal for 4 s indicates incorrect engine assembly. We urgently need to turn off the engine! If the pressure quickly stabilizes, the internal combustion engine is warmed up to operating temperature.
There should be no leaks upon visual inspection. In the first 3 minutes, the engine may knock: the hydraulic compensators are being pumped or the cups are running in. In the future, the sound should become uniform, without vibration. The appearance of a burning smell and slight smoke for the first start is normal - the assembly lubricants are burning through.
If the internal combustion engine is operating stably, start running-in. In order to properly run in the engine after a major overhaul, you need to understand the nuances of the test.