Brake pressure regulator, or how the sorcerer works on VAZ cars
A brake force regulator, or sorcerer in common parlance, is a mechanical device designed to relieve excess pressure in the rear drum brakes.
On VAZ-2109, VAZ-2108, VAZ-2114 and other front-wheel drive models produced in Togliatti, it was installed in the rear left part of the body, under the bottom, in front of the rear suspension beam. The brake pressure regulator on the VAZ-2107 model and other “classics” is located on the right in the direction of travel of the car.
New vehicles equipped with ABS and EBD do not use the sorcerer.
Brake pressure regulator: Secret "sorcerer"
Why do you need a brake pressure regulator?
| On my Ford Sierra, a unit similar to the one that is commonly called a “sorcerer” is mounted in the brake line. But it is not located under the bottom of the car, but in the engine compartment, and no mechanical rods are connected to it. What role does this device perform? Maybe this is an extra part and should be dismantled? Stanislav, Ternopil |
On passenger cars with a hydraulic brake system without an ABS anti-lock braking system, a pressure regulator is used in the rear mechanism circuit. Indeed, some car owners call it a “sorcerer”, considering it a mysterious and even useless device. In fact, this is an important element of the braking system, which, under all permissible vehicle loading options during emergency braking, prevents the rear wheels from locking ahead of the front wheels.
Pressure regulators can be controlled or uncontrolled. The operating principle of the former is an automatic change in the amount of braking force in the brake mechanisms of the rear wheels, depending on the intensity of braking and the vehicle load. The operation of such a device is controlled by a mechanical drive connected to the rear suspension or axle of the vehicle. During intense braking, which causes a longitudinal roll of the car and unloading of the rear wheels, the fluid supply to the rear mechanisms is cut off. This, in fact, prevents wheel locking.
The pressure regulator of the second type does not have a rigid mechanical connection with the suspension. Its correct name is unloading valve. It also limits the force transmitted from the master cylinder to the rear brakes. This “sorcerer” is triggered at a certain pressure value in the vehicle’s hydraulic system, which depends on the intensity of pressing the brake pedal.
It is impossible to remove (“suppress”) the unloading valve from the brake line, otherwise the distribution of braking force along the axles is disrupted (usually 60:40), and in the event of emergency braking, due to the blocking of the rear wheels, the likelihood of skidding of the rear axle of the car when moving along a curved path increases .
It should be noted that this unit is practically irreparable and does not require maintenance.
Prepared by Yuri Datsyk, Sergei Ivanov, Vladimir Kornitsky Photo by Sergei Kuzmich, Andrey Yatsulyak
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Why do you need a brake force regulator?
The function of the regulator is to temporarily reduce the braking force during heavy braking. The fact is that force evenly distributed on the rear and front axles can lead to a skid of the car. If the rear brakes start working a little later and weaker than the front ones, this does not happen.
Based on the above, we can conclude that the sorcerer is an element of the car’s safety system, partly preserving its stability on the road when the brake pedal is pressed in an emergency. On modern models, this function is performed by ABS. That is why there is no need today to use a technically outdated device in production.
How does the brake force regulator - sorcerer - work?
What is the "Sorcerer" for? This is a rather mysterious detail and no one has found a clear answer to this question. Perhaps this is why he was colloquially called a “sorcerer”, because he works magically. At its core, this part performs a similar function to the anti-lock braking system, preventing the wheels of the rear axle from locking during emergency braking. Its operation directly depends on the position of the rear axle relative to the car body: when braking sharply, the car nose-dives, and the rear part of the body rises, after which the “witchcraft” begins - the brake force regulator partially blocks the flow of fluid, and the rear wheels do not lock.
Of course, in ideal conditions (dry asphalt, straight road, working brake system and chassis), the brake force regulator does its job perfectly. But such conditions do not always occur.
How does a sorcerer work?
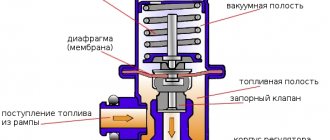
The regulator itself consists of a cylinder, valve, spring and rod. The latter is connected to the rear beam, which ensures the operation of the VAZ-2109 sorcerer. Also, brake fluid circuits pass through the rear brake pressure regulator. For their mounting on the device there are 4 threaded entries. » alt=»»> How does the sorcerer regulator work on a VAZ? During emergency braking, the front of the car is pressed to the ground, and the rear is raised. This causes the regulator rod to move, which blocks the flow of fluid to the rear cylinders. A spring located under the valve prevents it from closing completely. Therefore, the rear mechanisms still work, but later and weaker than the front ones.
Sorcerers in Slavic mythology
“The Arrival of a Sorcerer at a Peasant Wedding” (fragment).
V. Maksimov, 1875 The image of a sorcerer is known mainly in Eastern and Western Slavic demonology. In the Russian North, where ideas about a witch are weak, the sorcerer performs most of her functions. In the southern regions of Russia, Belarus and especially Ukraine, the sorcerer and the witch are often interchangeable characters with approximately the same set of functions. In the Carpathians, this character often breaks up into a number of fractional images, depending on the type of activity. In the Western Slavic tradition, where the practice of witchcraft was attributed primarily to the witch
, the image of a sorcerer is less developed than among the Eastern Slavs.
Among the southern Slavs, the image of a sorcerer is also poorly formed, since ideas about practicing magic and witchcraft are correlated either with female characters such as the veshtitsa, magician
, or with shepherds and other “knowledgeable ones”[4].
The image of a sorcerer among the Eastern Slavs was formed under the influence of ideas about the Magi - ancient Russian pagan priests who performed divine services, sacrifices and allegedly knew how to conjure the elements and predict the future [8]. Word of the Magus
akin to st.-slav.
vlasnѫti
“to speak confusedly, unclearly,” from which it follows that the Magi played the role of soothsayers and healers, whose main means of magical practice was the word [8].
Sorcerers can be werewolves[3]. From the “Tale of Bygone Years” it is known that Prince Vseslav of Polotsk’s mother gave birth to sorcery and the wise men imposed a nauz on his head
(magic knot), endowing him with the abilities of werewolf[8].
According to some ideas[3], as the death of a sorcerer approaches, evil spirits torment him, preventing him from dying until he passes on his abilities to his heirs. The death and funeral of a sorcerer is accompanied by a storm, whirlwind, and bad weather[9]. After the death of the sorcerer, an aspen stake should be driven into his corpse so that he does not become a ghoul[3].
Functions of a sorcerer
The functions of a sorcerer are universal: he is credited with the ability to influence all spheres of life, disrupt and restore their balance, create good and evil with the help of magical actions and means influencing atmospheric phenomena, crops, well-being and health of people, livestock, etc. [4 ]. It was believed that sorcerers could cast spells on people and livestock ( porchelniki
), sow discord between people, make creases in the field, destroying the harvest, send bad weather, pestilence, etc.[3]
In the Western Slavic tradition, the practice of witchcraft is assigned to the witch
, and the functions of a sorcerer are often limited to his professional activities (for example, witchcraft during hunting, shepherding)[4].
Possible malfunctions of the regulator
In general, there are few malfunctions that can occur in the sorcerer. These include:
- Valve jamming;
- Misalignment of position;
- Brake fluid leaks.
A deregulated sorcerer can be adjusted. You can determine the need for adjustment by the behavior of the car when you press the brake. If the regulator is set incorrectly, the car starts to toss to the side.
If the valve jams or fluid leaks, the mechanism must be replaced. Theoretically, it can be repaired. However, the process of such repairs is complex and expensive, which makes it unprofitable.
Replacing the brake pressure regulator
The replacement of the sorcerer on VAZ-2110 cars and other vehicles equipped with an RTD is carried out on an overpass. You need a 13 mm spanner, a powerful screwdriver and a special 10 mm wrench designed for unscrewing brake pipes. Before starting work, the assembly must be cleaned of dirt and rust, doused with WD-40 or another penetrating compound, and then wait half an hour.
Work begins by unscrewing the bolt securing the bracket to the spring. Afterwards, the brake pipes are dismantled, the position of which is recommended to be pre-marked.
You can also unscrew the tube fittings with a regular wrench. However, using a special tool makes the job easier and reduces the likelihood of “licking” the edges. After the fittings, unscrew the two bolts securing the sorcerer to the body and remove the part. » alt=»»> It is necessary to install the new VAZ-2110 sorcerer in strict reverse order. After installing it and before adjusting the RTD, you should bleed the rear brake circuits. Next, the above-described procedure for setting up the sorcerer is performed.
Brake force regulator - description and replacement
What is the "Sorcerer" for? This is a rather mysterious detail and no one has found a clear answer to this question. Perhaps this is why he was colloquially called a “sorcerer”, because he works magically.
At its core, this part performs a similar function to the anti-lock braking system, preventing the wheels of the rear axle from locking during emergency braking.
Its operation directly depends on the position of the rear axle relative to the car body: when braking sharply, the car nose-dives, and the rear part of the body rises, after which the “witchcraft” begins - the brake force regulator partially blocks the flow of fluid, and the rear wheels do not lock.
Of course, in ideal conditions (dry asphalt, straight road, working brake system and chassis), the brake force regulator does its job perfectly. But such conditions do not always occur.
Device Description
The design and principle of operation of this element are quite simple. At the moment when the rear part of the car body rises and the distance between the axle and the body increases, a special lever is activated, which is connected in a “sorcerer”. This lever lowers the piston, which closes the brake fluid channel, and accordingly the pressure on the rear pads decreases. The wheels do not stop rotating and, accordingly, do not skid.
The idea itself is quite clever, but, as often happens, in practice it raises doubts. After all, if when braking the brake pedal is pressed with great force, then the front wheels go into skid and the car still begins to skid. Quite often, when observing a traffic accident, you will notice that the cars with the “sorcerer” are turned backwards. Is this related to this miracle detail, which in its essence should prevent this skidding?
Signs of a malfunctioning brake force regulator
“Sorcerer”, as an element of the braking system, has a number of signs of malfunction that manifest themselves during emergency braking. Let's look at the first symptoms that call for checking the regulator:
- When braking hard, the car pulls to the side.
- Reduced braking efficiency (feels).
- “Bouncing” and jerking of the car when braking.
In such cases, it is necessary to check not only the “sorcerer”, but also other components of the brake system and chassis. But, since we are talking about the brake force regulator on the VAZ, we will consider this particular mechanism. After placing the car on a lift, pay attention to the regulator. The most common sign of its malfunction is the presence of brake fluid leaks. In case of any malfunction, the best solution is to replace the sorcerer. But, if you still decide to repair the brake force regulator, then below we have prepared brief instructions for this action.
Sorcerer repair
In order to repair the brake force regulator, you need to perform a number of actions:
- Dismantling. We remove the entire assembly, using wrenches 10 and 13. The brake pipes are unscrewed, the brake fluid is drained and plugs are installed in the pipes. Next, the “sorcerer” body is removed, which is attached to the bottom with two nuts.
- Diagnostics and replacement of “sorcerer” parts. Carefully examine the surface of the “Sorcerer”. If necessary, replace faulty parts (sealing rubber bands) using a repair kit. A soured piston cannot be repaired and requires a complete replacement of the unit.
- Installation of the sorcerer. Reassemble and adjust the part in reverse order and bleed the brake system. Add brake fluid.
Repairing this unit is a rather dubious decision. Therefore, we strongly recommend that in case of any malfunction, you perform such an action as replacing the brake force regulator.
Adjusting the braking forces of Lada Vesta
The operating principle of the system that regulates and distributes brake fluid pressure on Lada Vesta cars is fundamentally different from previous models, and there is no “witchcraft” in it. The Lada Vesta brake pressure regulator is directly connected to the ABS system and is electronically regulated depending on the speed of each wheel.
The ABS control unit transmits signals from speed sensors and analyzes the situation. The system “understands” any skidding and allows you to distribute the braking force with maximum efficiency. The pressure is controlled by the valves in the ABS hydraulic block, and there is no need for any magic. In addition, the electronics itself detects all malfunctions and reports them to the driver using a special lamp on the dashboard.
Loading…
Source: https://olade.ru/regulyator-tormoznyx-sil-opisanie-i-zamena
Examination
The operation of the VAZ-2109, 2110 and other AvtoVAZ models is checked on the move, in closed areas. To do this, accelerate the car to a speed of 40 km/h and sharply press the brake. The rear wheels should lock 1/2 second later than the front wheels.
The wheels are monitored by an assistant located outside the car. If wheel locking occurs noticeably later or does not occur at all, and also if the rear axle is locked simultaneously with the front, the sorcerer adjustment procedure is repeated.
To increase the response time of the rear brakes, the gap between the adjuster and the bracket is increased; to shorten it, it is reduced accordingly.
Examination
Symptoms of a sorcerer malfunction on a VAZ 2110 appear when braking:
- Pulling the car to the side;
- Skidding;
- Insufficient brake performance.
The VAZ 2110 has a sorcerer on a bracket under the bottom, slightly to the left, in the area of the rear wheels. It is better to work with it on a lift, overpass or inspection hole. The main defects are easily detected during external inspection. Brake fluid leaks indicate wear or damage to the seals.
Sorcerer (RDT) installed on the bottom
If the sorcerer's piston has turned sour and does not move, then this is also determined visually when the assistant smoothly presses the brake pedal several times. In both cases, repair is impractical and replacement is necessary.
Everything is in order if the regulator is clean, the gap between the drive lever and the plate is 2 mm, the rod moves when the pedal is pressed.
A good sorcerer must provide:
- Uniformity of braking forces on the rear wheels;
- Rear brakes engage later than front brakes;
- Adjustment of this delay, depending on the vehicle load.
Sorcerers in Slavic mythology[ | ]
“The Arrival of a Sorcerer at a Peasant Wedding” (fragment).
V. Maksimov, 1875 The image of a sorcerer is known mainly in Eastern and Western Slavic demonology. In the Russian North, where ideas about a witch are weak, the sorcerer performs most of her functions. In the southern regions of Russia, Belarus and especially Ukraine, the sorcerer and the witch are often interchangeable characters with approximately the same set of functions. In the Carpathians, this character often breaks up into a number of fractional images, depending on the type of activity. In the Western Slavic tradition, where the practice of witchcraft was attributed primarily to the witch
, the image of a sorcerer is less developed than among the Eastern Slavs.
Among the southern Slavs, the image of a sorcerer is also poorly formed, since ideas about practicing magic and witchcraft are correlated either with female characters such as the veshtitsa, magician
, or with shepherds and other “knowledgeable ones”[8].
The image of a sorcerer among the Eastern Slavs was formed under the influence of ideas about the Magi - ancient Russian pagan priests who performed divine services, sacrifices and allegedly knew how to conjure the elements and predict the future [9]. Word of the Magus
akin to st.-slav.
vlasnѫti
“to speak confusedly, unclearly,” from which it follows that the Magi played the role of soothsayers and healers, whose main means of magical practice was the word [9].
Sorcerers can be werewolves[3]. From the “Tale of Bygone Years” it is known that Prince Vseslav of Polotsk’s mother gave birth to sorcery and the wise men imposed a nauz on his head
(magic knot), endowing him with the abilities of werewolf[9].
According to some ideas[3], as the death of a sorcerer approaches, evil spirits torment him, preventing him from dying until he passes on his abilities to his heirs. The death and funeral of a sorcerer is accompanied by a storm, whirlwind, and bad weather[10]. After the death of the sorcerer, an aspen stake should be driven into his corpse so that he does not become a ghoul[3].
Functions of the sorcerer[ | ]
The functions of a sorcerer are universal: he is credited with the ability to influence all spheres of life, disrupt and restore their balance, create good and evil with the help of magical actions and means influencing atmospheric phenomena, crops, well-being and health of people, livestock, etc. [4 ]. It was believed that sorcerers could cast spells on people and livestock ( porchelniki
), sow discord between people, make creases in the field, destroying the harvest, send bad weather, pestilence, etc.[3]
In the Western Slavic tradition, the practice of witchcraft is assigned to the witch
, and the functions of a sorcerer are often limited to his professional activities (for example, witchcraft during hunting, shepherding)[4].
Removal and installation
To replace the sorcerer on a VAZ 2110, you need wrenches 13 and 10. Instead of 10, a special wrench for brake fittings is very desirable; it is more gentle than a regular open-end wrench when handling soft copper nuts due to the large contact area.
Replacing a wheel bearing in a garage is not difficult if you have the necessary tools on hand. The work procedure is presented here: https://vazweb.ru/desyatka/hodovaya/zamena-stupichnogo-podshipnika.html
This type of wrench is similar to a socket wrench, but has a slot for inserting a tube into it and high jaws. You need about half a liter of brake fluid and 4 rubber plugs for the brake hoses.
RTD (sorcerer) Fenox
AvtoVAZ cast iron and Belarusian aluminum regulators are sold in VAZ spare parts stores. Russian VIS is usually more reliable, Belarusian Fenox is lighter and cheaper.
RDT (sorcerer) VIS assembled
The conditions under the bottom are unfavorable for the sorcerer, so you first need to clean the dirt with a stiff brush and moisten the threaded connections with a penetrating lubricant such as WD-40. The fixing bracket is removed from the rear beam; if necessary, you can use a powerful screwdriver to loosen it.
Adjustment
The work of the sorcerer on VAZ cars depends on the position of the body. Therefore, adjustment must be performed not only during each maintenance, but also when replacing shock absorbers and springs, after repairing the rear beam and, of course, replacing the sorcerer itself.
The car is placed on an overpass or inspection hole, to set the suspension to a balanced position, the trunk is rocked a couple of times by hand. Use a 13mm wrench to loosen the fastening bolts to the bracket; the front bolt is not visible from below, you need to find it by touch.
By moving the regulator, a gap of 2 mm is achieved between the elastic plate (the rod rests against it) and the lever. The spring resistance is high, you need to use a “mounter” or a special device. The bolts are tightened and the gap is checked with a feeler gauge. If you don’t have a probe, you can use a drill with a diameter of 2 mm and even a two-ruble coin.
Further verification is carried out on the fly. When braking from a speed of 40 km/h, on your own or with the help of a partner outside the car, evaluate the moment when the rear mechanisms begin to operate in comparison with the front ones.
If it needs to be done later, then the gap must be increased, and if it is smaller, then, accordingly, reduced.
Setting up the brake force regulator: “The Sorcerer” carries the hero
November 18, 2010
“The sorcerer”, or, according to the catalogue, the pressure regulator in the brake drive, it was not for nothing that people received such an apt nickname: no one really knows how it works, but, they say, being faulty, it can present an unpleasant surprise - make the car dance in an emergency. braking.
This is where the insidiousness of the “sorcerer” lies: during normal operation, without braking to the floor, its work or inaction is practically not felt, but when its help is especially needed, it may not come.
The pistons have soured, the rod or drive lever has broken off, or you installed a new one instead of a faulty regulator, but for the time being you don’t know that the unit is defective or out of adjustment... How dangerous is this?
Let’s check in our experiment how “witchcraft” affects the effectiveness of the brakes at partial and full load of the Chevrolet Niva and Kalina and what the owner should be wary of if he does not monitor the condition of the regulator. We can simulate a malfunction, from excessive activity to complete inaction, with adjustments.
Let us remind you that the regulator’s task is to reduce the braking force on the rear axle, reducing the likelihood of skidding when braking to skid.
The regulator, mounted on the body and connected by an elastic lever to the axle beam, limits the pressure in the rear brake mechanisms depending on the position of the rear of the body relative to the road, that is, on the vehicle load.
“Sorcerer” is the predecessor of ABS, which allows to some extent prevent the rear wheels from locking when braking and thereby reduces the likelihood of skidding. “Sorcerer” is the predecessor of ABS, which allows to some extent prevent the rear wheels from locking when braking and thereby reduce the likelihood of skidding.
"CHEVROLE-NIVA"
By the way, before testing tires on cars without ABS, each time we slightly adjust the regulator taking into account the road condition (snow, ice, asphalt), ensuring that the rear wheels lock a little later than the front ones. Let's not break tradition. Our Shniva found the gap between the cheeks of the regulator to be 16 mm, which was adjusted using a stop screw.
Several brakings, and the braking distance from 80 km/h for a car with a partial load is determined: 34.4 m. With a full load... 33.6! Almost a meter shorter! At the same time, the driver noted a heavier pedal and rapid heating of the brakes, which required cooling before each measurement. Let’s remember these parameters and make adjustments to the “sorcerer” adjustment. First, let's reduce the gap to 8 mm. Now the regulator significantly limits the pressure in the rear brakes, transferring almost all the hard work to the front ones.
Braking has become more difficult, keeping the front wheels from skidding is not so easy - they lock very sharply and the car, naturally, loses control. However, the result, to our surprise, is the same as in the basic version: 34.4 m. At full load, you have to press the pedal much harder, the front brakes begin to overheat. The result is 37.8 m. This is 4.2 m more than with the basic adjustment (33.6 m).
"Chevrolet Niva"
The third state - we reduce the influence of the regulator by increasing the gap from the original one by 8 mm, that is, we set it to 24 mm. When there are two people in the car, the braking distance remains virtually unchanged - 34.3 m. However, now the rear wheels are blocked. But at full load the braking is very effective, the deceleration is easy to control and the result is a record: only 30.8 m!
- In the normal position of the regulator, as the vehicle's weight increases, its braking distance decreases - this affects the more complete use of the traction weight by the rear wheels.
- The best braking is at full load, when the regulator minimally limits the pressure in the rear brakes.
- However, at partial load this can lead to skidding. The high center of gravity and short wheelbase of the Shnivy contribute to a significant redistribution of mass during braking, therefore, at partial load, the contribution of the rear axle to braking is small.
"LADA KALINA"
We set the regulator so that the rear is slightly late in locking the wheels. With this setting and partial load, the car needed only 27 m to stop. Fully loaded - 29.5 m. There are slight difficulties in preventing the front wheels from skidding. We reduce the gap in the regulator to zero - the half-empty Kalina stops after 31.8 m. The braking distance increases by 4.8 m, accompanied by a sharp blocking of the front wheels. The loaded one slows down after 35.2 m, the deterioration is even greater - 5.7 m! The pedal effort is increased and the brakes become noticeably hot.
Now we move the adjuster so that the rear brakes work as efficiently as possible. At partial load, the rear wheels suddenly lock and the car drifts off course—you have to release the pedal. On the verge of blocking it is very difficult to brake. The result is 30 m, which is 3 m worse than the “norm”.
Full load gave a result of 26.9 m, which is 2.6 m better than the base (29.5 m). There are no comments regarding deceleration control. At the basic position of the regulator, the braking distance increases with increasing load. At partial load the spread of results is 4.8 m, so the base position is most effective.
When you deviate from it in any direction, the braking distance increases.
- On a fully loaded vehicle, depending on the position of the regulator, the spread of the braking distance is 8.3 m.
- The best results, as on the Niva, come with increasing pressure in the rear brakes.
- However, on a slippery road, even in smooth turns, early locking of the rear wheels is possible, leading to a skid.
- And at partial load, with the regulator position different from the base one, the braking distance only increases.